ECG quiz: Palpitations, irregular pulse on diabetic review and blackouts
As part of a series on Pulse, Dr Yassir Javaid, a GPwSI in cardiology and echocardiography, asks what these ECGs could signify. See bottom of the page for answers
Question 1
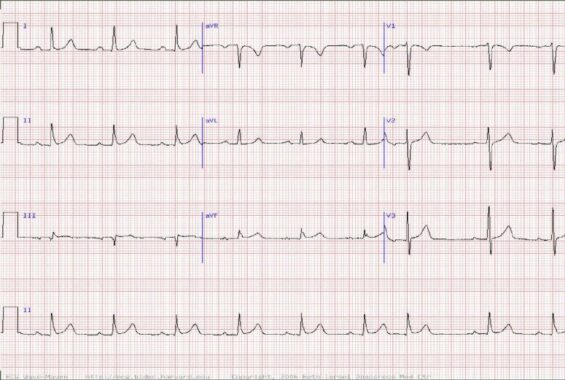
You see a 30 year old overweight patient c/o palpitations. What does his ECG show?
A Sinus with a single premature ventricular complex
B Sinus with SA exit block
C Sinus with A-V Wenckebach
D Sinus with a single premature atrial complex
E Respiratory sinus arrhythmia
Question 2
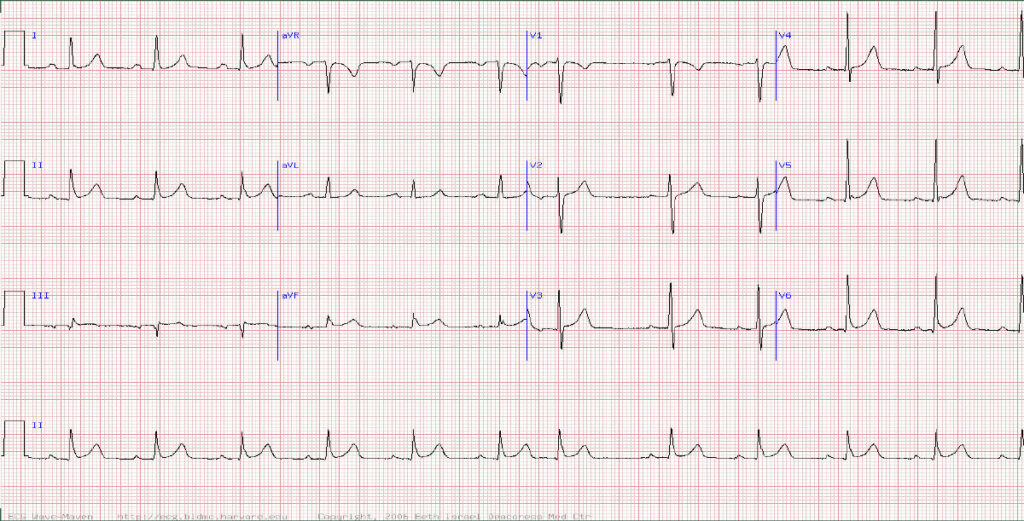
What is the rhythm in this 68 year-old female who attends for a diabetic review and is found to have an irregular pulse?

A Multifocal atrial tachycardia
B Wandering atrial pacemaker
C Atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response
D Atrial flutter with rapid ventricular response
E Sinus arrhythmia with tremor artefact
Question 3
This 81 year old woman presents to her GP with blackouts lasting a few seconds. What does her ECG show?
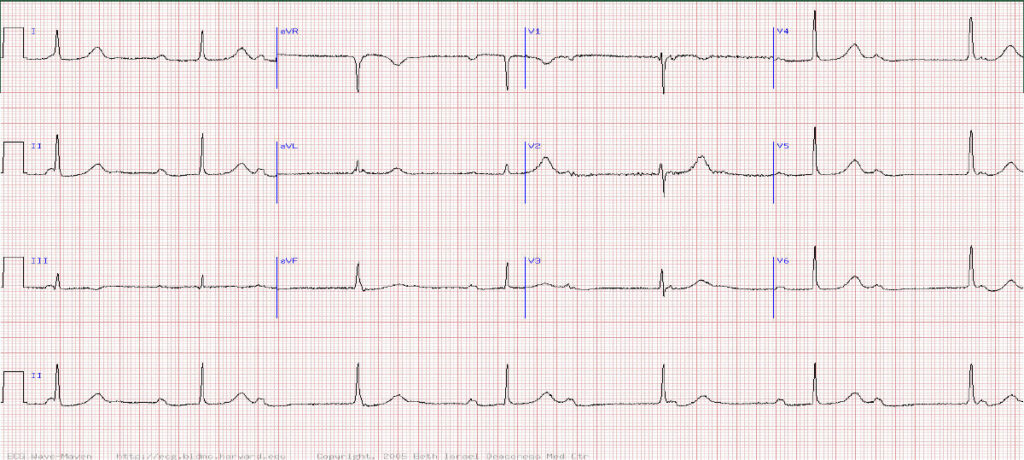
A Sinus rhythm with Mobitz I second degree (Wenckebach) AV block
B Sinus rhythm with Mobitz II AV block
C Sinus rhythm with no AV dissociation
D Sinus rhythm with third degree (complete) AV block and a junctional escape pacemaker
E Atrial tachycardia with complete heart block
Answers
Question 1 Sinus with a single premature atrial complex
Explanation
The ECG shows consistent p waves and each p wave is followed by a qrs complex, indicating normal sinus rhythm with no high degree heart block.
There is however one QRS complex in the middle of the rhythm strip which does not have a preceding p wave. This indicates an atrial ectopic which is likely generated from atrial tissue close to the AV node and hence no p wave.
Patients with frequent atrial ectopics should be advised to aim for a healthy lifestyle and good BP control. Patients who are particularly symptomatic can be offered a beta blocker.
Question 2 Atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response
Explanation
Atrial fibrillation becomes increasingly common in people over 65 particularly with comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes and obesity.
The Ecg reveals no consistent p waves and an irregular ventricular (QRS) response confirming the diagnosis.
TIP The QRS amplitude in AF is often variable
Question 3 Sinus rhythm with third degree (complete) AV block and a junctional escape pacemaker
Explanation
High degree heart block (second degree type 2 or 3rd degree) should be suspected in any elderly patient with presyncope or syncope.
The Ecg reveals regular p waves (so normal sinoatrial node function) as well as a regular QRS rhythm. However, there is no relationship between the 2 indicating a complete atrioventricular block. The slow regular QRS rhythm represents an escape rhythm. Because the QRS is narrow, the escape rhythm is likely to be generated near the level of the AV node ie junctional.
TIP Patients with complete heart block are at high risk of sudden death and should be considered for admission for urgent pacemaker insertion
Pulse July survey
Take our July 2025 survey to potentially win £1.000 worth of tokens

Visit Pulse Reference for details on 140 symptoms, including easily searchable symptoms and categories, offering you a free platform to check symptoms and receive potential diagnoses during consultations.
Related Articles
READERS' COMMENTS [1]
Please note, only GPs are permitted to add comments to articles












Thanks, but if my patients have symptomatic arrhythmias they need to see an actual cardiologist.