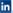After a few days of illness the concentration of the virus falls
This information is sourced from the UK Research and Innovation Website (UKRI):
Testing during the course of infection:
- The test for the virus detects the genetic material (nucleic acid) of the virus during an active infection. It is also called a PCR test or nucleic acid test
- The coronavirus can be detected in swabs taken from the nose or throat, even before symptoms of illness first appear
- The nucleic acid test is most reliable and can be used in the first 7 days of illness
- The test might be unreliable between days 7-10
- Some people have no symptoms throughout their infection but are positive on the virus test and infectious to others
The antibody test (blood test):
- Will only detect infections after the immune system has produced antibodies that recognise the virus
- This happens approximately 7–10 days after symptoms develop
- There is a clear link between the presence of the antibody and protective immunity for many common viral infections
- This link has not yet been confirmed for the new coronavirus
- It is possible that people are temporarily protected against reinfection but that the protection wanes with time